Focus-A modernisation on transitional old story
Acton
Roles-Little red Ridding hood,Witch,Baker,Jack.
Time-¨medieval¨ (14) but unreal once upon a time.
Tension-problem: the curse.
Space-where,village,coste,woods.

chemical potential energy
 In thermodynamics, chemical potential, also known as partial molar free energy, is a form of potential energy that can be absorbed or released during a chemical reaction or phase transition
electrical energy
In thermodynamics, chemical potential, also known as partial molar free energy, is a form of potential energy that can be absorbed or released during a chemical reaction or phase transition
electrical energy

Electric energy is the energy created by electrons moving through an electrical conductor. The world is made of matter. All matter contains atoms that contain electrons that are always moving. When electrons are forced down a conductive path, such as a wire, the movement produces electricity, or electric energy.
gravitational potential energy
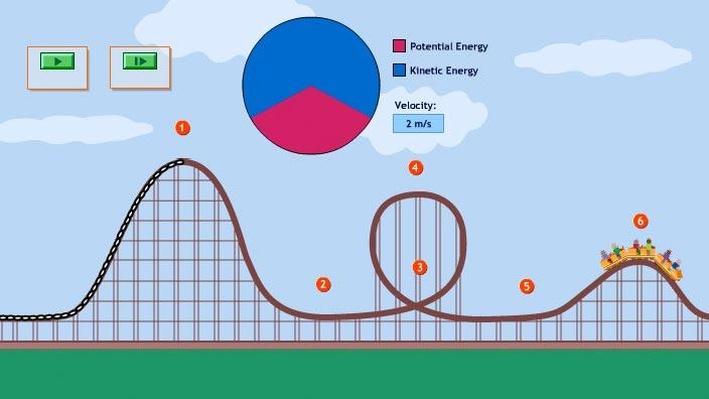 Gravitational potential energy is energy an object possesses because of its position in a gravitational field. The most common use of gravitational potential energy is for an object near the surface of the Earth where the gravitational acceleration can be assumed to be constant at about 9.8 m/s2
Gravitational potential energy is energy an object possesses because of its position in a gravitational field. The most common use of gravitational potential energy is for an object near the surface of the Earth where the gravitational acceleration can be assumed to be constant at about 9.8 m/s2
heat energy

Heat energy is the result of the movement of tiny particles called atoms molecules or ions in solids, liquids and gases. Heat energy can be transferred from one object to another, and the transfer or flow due to the difference in temperature between the two objects is called heat.Nov 20, 2009
light energy

Light energy is the only form of energy that we can actually see directly. It is formed through chemical, radiation, and mechanical means. Light energy can also be converted into other forms of energy. Interesting Light Energy Facts: Light travels at a speed of about 300,000 km/s.
sound energy
 Sound energy is a form of energy that is associated with vibrations of matter. It is a type of mechanical wave which means it requires an object to travel through. This object includes air and water. Sound originates from the vibrations that result after an object applies a force to another object.
Sound energy is a form of energy that is associated with vibrations of matter. It is a type of mechanical wave which means it requires an object to travel through. This object includes air and water. Sound originates from the vibrations that result after an object applies a force to another object.
kinetic energy
 In
In physics
, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy
that it possesses due to its motion
. It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity
Having gained this energy during its acceleration
, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes. The same amount of work is done by the body in decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest.
elastic potential energy
 Elastic potential energy is Potential energy stored as a result of deformation of an elastic object, such as the stretching of a spring. It is equal to the work done to stretch the spring, which depends upon the spring constant k as well as the distance stretched.
Elastic potential energy is Potential energy stored as a result of deformation of an elastic object, such as the stretching of a spring. It is equal to the work done to stretch the spring, which depends upon the spring constant k as well as the distance stretched.









